Mucic acid
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
D-Galactaric acid[1]
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S,3R,4S,5R)-2,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxyhexanedioic acid | |
| Other names
Galactaric acid; Galactosaccharic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.641 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O8 | |
| Molar mass | 210.138 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 230 °C (446 °F; 503 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Mucic acid, C6H10O8 or HOOC-(CHOH)4-COOH (galactaric acid or meso-galactaric acid) is an aldaric acid obtained by nitric acid oxidation of galactose or galactose-containing compounds such as lactose, dulcite, quercite, and most varieties of gum.[2]
Properties
[edit]Mucic acid forms a crystalline powder, which melts at 210–230 °C.[3] It is insoluble in alcohol, and nearly insoluble in cold water.[2] Due to the symmetry in the molecule, it is optically inactive even though it has chiral carbon atoms (i.e., it is a meso compound).
Reactions
[edit]When heated with pyridine to 140 °C, it is converted into allomucic acid.[2][4] When digested with fuming hydrochloric acid for some time it is converted into αα′ furfural dicarboxylic acid while on heating with barium sulfide it is transformed into α-thiophene carboxylic acid.[2] The ammonium salt yields on dry distillation carbon dioxide, ammonia, pyrrol and other substances.[2] The acid when fused with caustic alkalis yields oxalic acid.[2]
With potassium bisulfate mucic acid forms 3-hydroxy-2-pyrone by dehydration and decarboxylation.
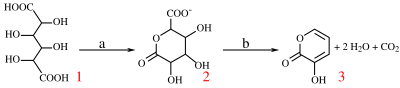
Reaction of mucic acid to 3-hydroxy-2-pyrone with a) potassium bisulfate 160 °C / 4 hrs. b) hydrochloric acid to pH = 7
Use
[edit]Mucic acid can be used to replace tartaric acid in self-raising flour or fizzies.
It has been used as a precursor of adipic acid in the way to nylon by a rhenium-catalyzed deoxydehydration reaction.[5]
It has been used as a precursor of Taxol in Nicolaou Taxol total synthesis (1994).
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ https://iupac.qmul.ac.uk/2carb/23.html
- ^ a b c d e f Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 18 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 954.
- ^ "Mucic acid". ChemSpider. Retrieved 30 March 2018.
- ^ Butler, C. L.; Cretcher, L. H. (1929). "The Preparation of Allomucic Acid and Certain of Its Derivatives". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 51 (7): 2167. doi:10.1021/ja01382a029.
- ^ Li, X.; Wu, D.; Lu, T.; Yi, G.; Su, H.; Zhang, Y. (2014). "Highly Efficient Chemical Process to Convert Mucic Acid into Adipic Acid and DFT Studies of the Mechanism of the Rhenium-Catalyzed Deoxydehydration". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 53 (16): 4200–4204. doi:10.1002/anie.201310991. PMID 24623498.

